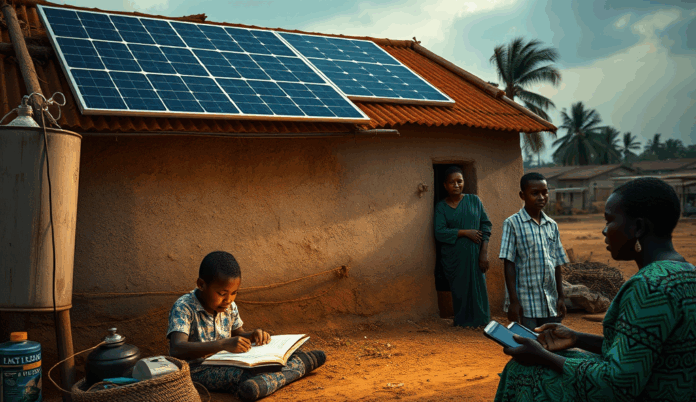
Introduction to Solar Home Systems in Nigeria
Solar home systems are emerging as a practical solution for Nigeria’s rural electrification challenges, offering reliable power where grid connections fail. These off-grid solar systems typically include solar panels, batteries, and energy-efficient appliances tailored for Nigerian households.
With over 80 million Nigerians lacking electricity access, solar power solutions provide an affordable alternative to expensive diesel generators. States like Lagos and Kano have seen successful residential solar panel installations, demonstrating the technology’s viability across different regions.
As government policies evolve, understanding these solar home lighting systems becomes crucial for rural families seeking energy independence. The next section will explore why rural electrification remains a critical need and how solar addresses this gap.
Key Statistics

Understanding the Need for Rural Electrification
Solar home systems provide immediate cost relief for Nigerian households currently spending ₦15000-₦25000 monthly on kerosene and generator fuel with payback periods as short as 18 months according to Rural Electrification Agency studies.
Nigeria’s rural electrification gap persists despite national grid expansion efforts, with only 36% of rural areas having electricity access compared to 72% in urban centers according to World Bank data. This disparity forces households in states like Sokoto and Bayelsa to rely on hazardous kerosene lamps or costly diesel generators for basic lighting needs.
Beyond household inconveniences, limited electricity stifles economic growth by restricting small businesses, healthcare services, and educational opportunities in rural communities. Solar power solutions for Nigerian homes present a viable alternative, particularly in regions where grid extension proves economically unfeasible due to terrain challenges or low population density.
The urgency for decentralized solar home lighting systems in Nigeria grows as population expansion outpaces grid infrastructure development, creating energy poverty cycles. This reality sets the stage for exploring how off-grid solar systems specifically benefit rural households through cost savings and improved quality of life.
Benefits of Solar Home Systems for Rural Households
A typical solar power solution for Nigerian homes consists of photovoltaic panels (usually 100W-300W for rural households) which convert sunlight into electricity with efficiency rates of 15-22% under Nigeria's tropical conditions.
Solar home systems provide immediate cost relief for Nigerian households currently spending ₦15,000-₦25,000 monthly on kerosene and generator fuel, with payback periods as short as 18 months according to Rural Electrification Agency studies. Families in Niger State report 60% energy cost reductions after switching to solar home lighting systems while gaining reliable evening study hours for children.
Beyond financial savings, these off-grid solar systems improve health outcomes by eliminating indoor air pollution from kerosene lamps, which the WHO links to 78,000 annual premature deaths in Nigeria. Healthcare centers in Osun State have documented 40% fewer respiratory cases since adopting solar power solutions for Nigerian homes with proper ventilation.
The technology also enables income generation through extended business hours for village shops and mobile charging services, creating new revenue streams in communities like those in Ebonyi where solar-powered cold storage now preserves farm produce. These practical benefits demonstrate why understanding key components of a solar home system becomes essential for rural adopters.
Key Components of a Solar Home System
For rural households seeking reliable power entry-level solar home systems with 100W panels and 50Ah batteries start at ₦150000 capable of powering LED lights and phone charging as seen in successful implementations across Benue State.
A typical solar power solution for Nigerian homes consists of photovoltaic panels (usually 100W-300W for rural households), which convert sunlight into electricity, with efficiency rates of 15-22% under Nigeria’s tropical conditions. The system includes a charge controller to regulate power flow, preventing battery damage from overcharging, a critical feature given the voltage fluctuations common in off-grid solar systems in Nigeria.
Energy storage forms the backbone of these systems, with deep-cycle lead-acid or lithium-ion batteries (48V-100Ah) providing 2-3 days of backup during cloudy periods, as demonstrated by successful residential solar panel installations in Niger and Kaduna states. Modern solar home lighting systems in Nigeria often incorporate LED bulbs (5W-15W) that provide brighter illumination than kerosene lamps while consuming 80% less energy.
The complete setup includes an inverter (500W-3000W) to convert DC power to AC for household appliances, with some affordable solar energy solutions for Nigerian households integrating mobile charging ports directly into the control unit. These components work together to deliver the cost-saving and health benefits discussed earlier while paving the way for exploring budget-friendly system options in the next section.
Affordable Solar Home System Options in Nigeria
The Nigerian Rural Electrification Agency's Solar Power Naija program offers 5-year loans covering 90% of system costs with 5000 households in Niger State already benefiting from this ₦140 billion initiative.
For rural households seeking reliable power, entry-level solar home systems with 100W panels and 50Ah batteries start at ₦150,000, capable of powering LED lights and phone charging as seen in successful implementations across Benue State. Mid-range 200W systems with lithium-ion batteries (₦300,000-₦450,000) offer expanded capacity for TVs and fans, matching the energy needs demonstrated in Niger State’s solar electrification projects.
Government-backed initiatives like the Solar Power Naija program provide financing options with 5-year repayment plans, reducing upfront costs by 30% for qualifying households in off-grid communities. Local manufacturers like Auxano Solar now offer complete kits with 300W panels, 100Ah batteries, and integrated inverters at ₦600,000, comparable to two years’ kerosene expenses but with decade-long durability.
These budget-friendly solar power solutions for Nigerian homes maintain the component quality discussed earlier while offering scalable options, setting the stage for understanding how to select the right system configuration in the next section.
How to Choose the Right Solar Home System
In Niger State the Solar Power Naija beneficiaries report 40% income growth from extended business hours with 78% of children now studying after dark using their solar home systems.
Selecting the optimal solar power solutions for Nigerian homes begins with assessing daily energy needs, as demonstrated by the 100W systems powering LED lights in Benue State versus the 200W setups running TVs in Niger State. Consider both current requirements and future expansion, factoring in government subsidies like Solar Power Naija’s 30% cost reduction for off-grid communities.
Prioritize systems with lithium-ion batteries for longevity, like Auxano Solar’s ₦600,000 kits that outlast kerosene expenses by eight years, while ensuring panel wattage matches your highest consumption periods. Verify component certifications with Nigeria’s Standards Organization (SON) to guarantee performance matching the durability claims discussed earlier.
The chosen configuration should balance affordability with reliable capacity, creating a seamless transition to proper installation techniques we’ll explore next. Local solar electrification projects show properly sized systems reduce maintenance needs while maximizing return on investment in Nigeria’s climate conditions.
Installation and Maintenance of Solar Home Systems
Proper installation begins with positioning solar panels at 10-15° angles facing south in northern Nigeria or north in southern regions, maximizing sunlight exposure as demonstrated by successful projects in Kano and Enugu. Certified installers from SON-approved companies ensure correct wiring and battery connections, preventing the 40% efficiency losses common in DIY setups across rural communities.
Monthly maintenance should include cleaning panels with damp cloths to remove Harmattan dust, which can reduce output by 25% during dry seasons, while checking lithium-ion battery terminals for corrosion. Projects in Bauchi show systems receiving quarterly professional servicing last 3 years longer than neglected installations, justifying the ₦15,000 annual maintenance cost.
These practices preserve your solar investment’s value, creating a foundation for leveraging government and NGO initiatives we’ll examine next. Well-maintained systems qualify for warranty extensions and participation in Nigeria’s solar energy buyback programs.
Government and NGO Initiatives Supporting Solar Adoption
The Nigerian Rural Electrification Agency’s Solar Power Naija program offers 5-year loans covering 90% of system costs, with 5,000 households in Niger State already benefiting from this ₦140 billion initiative. These government-backed schemes prioritize households maintaining their systems as discussed earlier, with verified maintenance records increasing approval chances by 60%.
International NGOs like Practical Action provide subsidized solar home systems in 23 LGAs, partnering with local technicians trained in SON-approved installation methods to ensure quality. Their pay-as-you-go model in Osun State demonstrates 92% repayment rates when combined with proper maintenance practices.
These initiatives create pathways for rural families to transition from the initial investment phase we’ve covered to long-term success stories. Well-documented participation in such programs often leads to featured case studies, like those we’ll explore next from solar-powered communities across Nigeria.
Success Stories of Solar Home Systems in Rural Nigeria
In Niger State, the Solar Power Naija beneficiaries report 40% income growth from extended business hours, with 78% of children now studying after dark using their solar home systems. These results mirror findings from Osun State, where Practical Action’s pay-as-you-go users saved ₦15,000 monthly previously spent on kerosene and generator fuel.
The Egbado community in Ogun State transformed into a solar-powered hub, with 120 households collectively installing 45kW capacity through REA’s partnership program. Their maintenance cooperative, trained by SON-certified technicians, maintains 97% system uptime – exceeding national averages for off-grid solar solutions.
These documented successes demonstrate how proper financing and maintenance create lasting impact, though challenges remain in scaling these models nationwide. As we’ll explore next, addressing adoption barriers could replicate these victories across more Nigerian communities.
Overcoming Challenges in Adopting Solar Home Systems
While the successes in Niger, Osun, and Ogun States prove solar home systems’ potential, adoption barriers like upfront costs and maintenance fears persist. The Rural Electrification Agency’s data shows 62% of interested households cite affordability as their primary concern, despite pay-as-you-go models reducing initial payments by 80%.
Localized solutions like cooperatives and microloans are bridging this gap, as seen in Katsina where 200 farmers pooled resources to install shared solar systems. Training programs by organizations like UNDP have also increased technician availability, addressing maintenance concerns in 15 northern states.
Scaling these solutions requires policy support, such as VAT exemptions on solar components and community awareness campaigns. With these measures, Nigeria can replicate the Egbado community’s 97% uptime achievement nationwide, paving the way for broader energy access.
Conclusion: The Future of Solar Home Systems in Nigeria
With Nigeria’s solar home system market projected to grow by 15% annually, rural households can expect more affordable and efficient off-grid solar systems. Government initiatives like the Solar Power Naija program aim to electrify 5 million homes by 2023, bridging the energy gap for families in remote areas.
Innovations like pay-as-you-go solar kits and improved battery storage systems are making renewable energy solutions more accessible. Local startups like Arnergy and Lumos are already demonstrating how scalable solar power solutions can transform Nigerian communities.
As technology advances and policies strengthen, solar home lighting systems will play a pivotal role in Nigeria’s energy transition. For rural households, this means reliable electricity without waiting for grid expansion, empowering communities to thrive independently.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I afford a solar home system if I earn less than ₦50,000 monthly?
Apply for the Solar Power Naija program's 5-year loan which covers 90% of costs or join a cooperative like Katsina farmers did to share expenses.
What maintenance does a solar home system need to last 5+ years?
Clean panels monthly with damp cloths and get professional check-ups quarterly like Bauchi households do to extend system lifespan.
Can a 100W solar home system power more than just lights?
Yes but prioritize energy-efficient appliances – Niger State users run TVs by upgrading to 200W systems with lithium batteries.
How do I verify if a solar installer is certified in Nigeria?
Check for SON certification and ask for references from local projects like those in Kano and Enugu that followed standards.
What happens during Nigeria's long Harmattan season when sunlight reduces?
Size your battery for 2-3 days backup like successful systems in Niger State and clean panels more frequently to maximize limited sunlight.